IARRP team develops quantum dot magnetic biochar composite material for visible light degradation of tetracycline
The Innovation Team of Soil-Plant Interactions at the Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning (IARRP) of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) has made significant progress in antibiotic pollution control and agricultural waste resource utilization technology.
The related research, titled "Adsorptive-photocatalytic removal of tetracycline from wastewater by Fe3O4 and SnO2-containing biochar nanocomposites," has been published in the leading soil science journal, Biochar (IF=13.1).
Tetracycline is the most commonly used antibiotic for human and animal use, widely applied in medical treatment and livestock breeding due to its advantages of broad spectrum, high efficiency, and low cost. With the excessive and continuous use of tetracycline, its emission has far exceeded the environment's carrying capacity, leading to a series of emerging pollution issues that threaten human health and safety, such as bacterial resistance and resistant genes, etc., and there is an urgent need to develop green, highly efficient, and recyclable treatment materials.
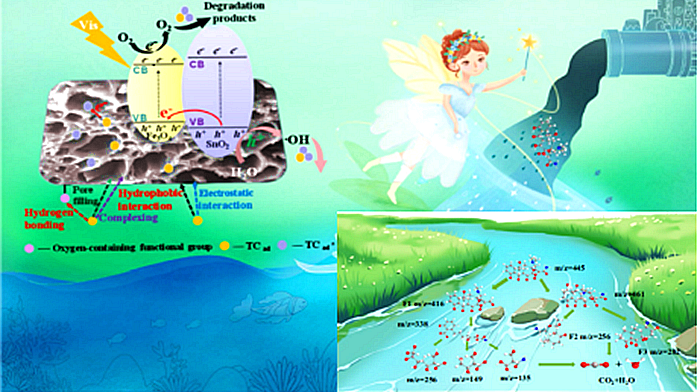
In this study, wheat straw was used as the biomass material to synthesize quantum dot magnetic biochar composite (BC@Fe3O4@SnO2) through impregnation pyrolysis technology. Under the visible light condition, the composite material could remove 91.80% of tetracycline in 3 h, and 82.33% of tetracycline in pharmaceutical wastewater, far superior to the original biochar and nano-metal particles. Moreover, it can be recycled many times with stable properties. Density functional theory calculations indicated that the removal mechanism of tetracycline by the composite involved π-π interactions and complexation. The modification of metal nanoparticles enhanced the material's binding energy, and generated a large number of positive charges on the surface of Fe/Sn-biochar, which promoted the catalytic degradation of tetracycline. OH and O2- were the main active substances. In this study, the synergistic coupling of adsorption and photocatalytic technology was realized, which provided a new strategy for the efficient degradation of tetracycline and revealed the mechanism of interaction between the composite material and tetracycline from the microscopic perspective, as well as provided a new idea for the resourceful utilization of agricultural waste.
M.S. Zhang Chuchen and Dr. Zhao Shuwen from the Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) were the co-first authors of the paper, with Professor Zhang Qianru as the corresponding author. The research received funding from the National Key Laboratory for Efficient Utilization of Dryland and Semi-Arid Farmland in Northern China, the Major Task of the Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the China-Korea Young Scientists Exchange Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology.
Citation:
Zhang C.C., Zhao S.W., Huang Q.L., Liu J.Q, Zhang Q.R. 2025. Adsorptive-photocatalytic removal of tetracycline from wastewater by Fe3O4 and SnO2-containing biochar nanocomposites. Biochar. 7:38.
Original Article Link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-024-00420-4
-
 Jun 05, 2025CAAS President Meets New FAO Representative in China
Jun 05, 2025CAAS President Meets New FAO Representative in China -
 May 27, 2025Director General of IARRP attends 2025 Global Forum of Group on Earth Observations
May 27, 2025Director General of IARRP attends 2025 Global Forum of Group on Earth Observations -
 May 20, 2025IPPCAAS Experts Visit Australia to Promote In-Depth China–Australia Cooperation in Plant Biosafety
May 20, 2025IPPCAAS Experts Visit Australia to Promote In-Depth China–Australia Cooperation in Plant Biosafety -
 May 20, 2025Opening Ceremony of the Seminar on Modern Breeding and Management of the Vegetable Industry for BRI Partner Countries Successfully Held in Yanqing, Beijing
May 20, 2025Opening Ceremony of the Seminar on Modern Breeding and Management of the Vegetable Industry for BRI Partner Countries Successfully Held in Yanqing, Beijing -
 May 18, 2025Sustainable Dairy Development — The 9th International Symposium on Dairy Cow Nutrition and Milk Quality Convenes in Beijing
May 18, 2025Sustainable Dairy Development — The 9th International Symposium on Dairy Cow Nutrition and Milk Quality Convenes in Beijing
