Findings on the mechanisms of key organic carbon molecules specifically promoting arsenic methylation in paddy soils
Recently, the Remediation of Degraded and Contaminated Farmland Team of the Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences revealed the mechanism of selective utilization of organic carbon molecules to promote arsenic methylation by increasing the activity of arsM -carrying microbial methyltransferase in paddy soils. Relevant research results have been published in Soil Biology and Biochemistry .
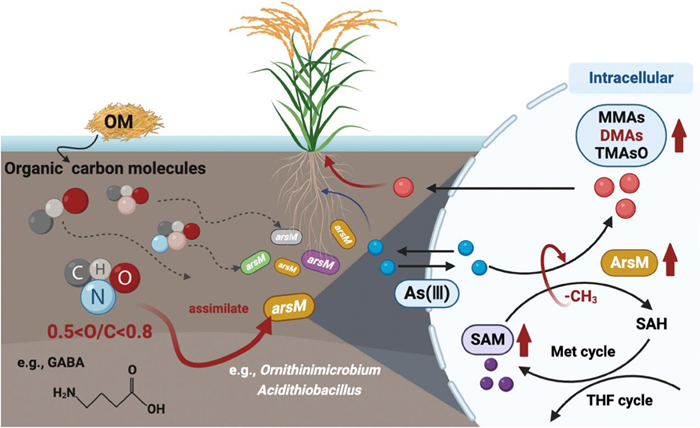
Excessive accumulation of methylated arsenic in rice grain husks can easily induce straight-head disease, leading to incomplete grain filling and causing yield reduction or even complete crop failure. The application of different organic materials in paddy fields can differentially stimulate the arsenic methylation process, thereby increasing the risk of straight-head disease in rice. However, it is unclear how the properties of different organic carbon molecules influence the key microbial mechanisms of arsenic methylation.
The study found that microorganisms that mediate arsenic methylation in paddy soils are significantly regulated by organic carbon molecules, and there is a significant specific correlation between them. Among them, CHON molecules with the atomic oxygen to carbon ratio (O/C) ranging from 0.5 to 0.8 can significantly stimulate the arsenic methylation process. This is mainly because it increases the content of crucial intracellular S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), the methyl donor for arsenic, and the activity of its methyltransferase (ArsM), thereby increasing the arsenic methylation efficiency. This study provides theoretical support for predicting the occurrence of rice straight-head disease in the future and provides scientific guidance for safe production in paddy fields.
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science and the special fund for Science and Technology Innovation Teams of Shanxi Province.
linkage: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109305
-
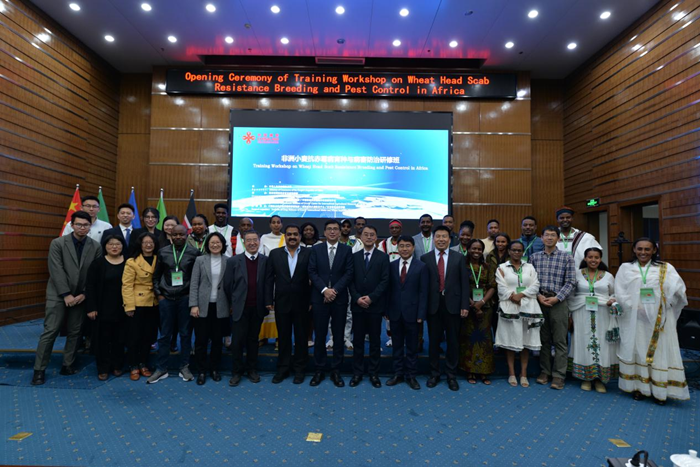 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
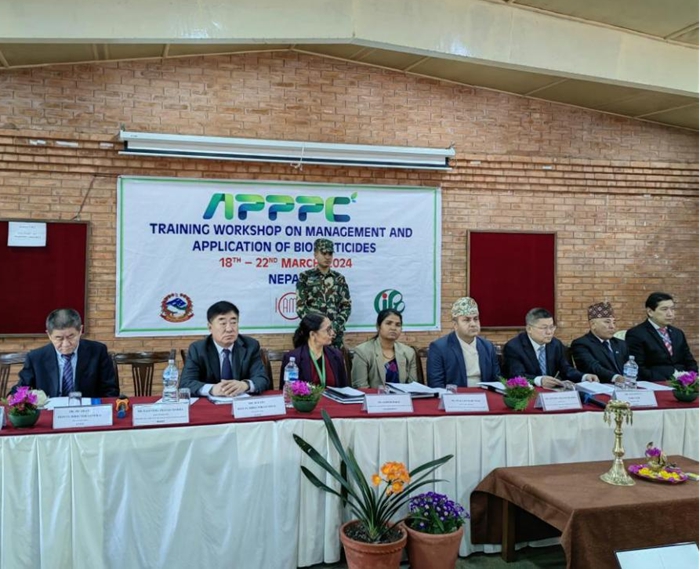 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
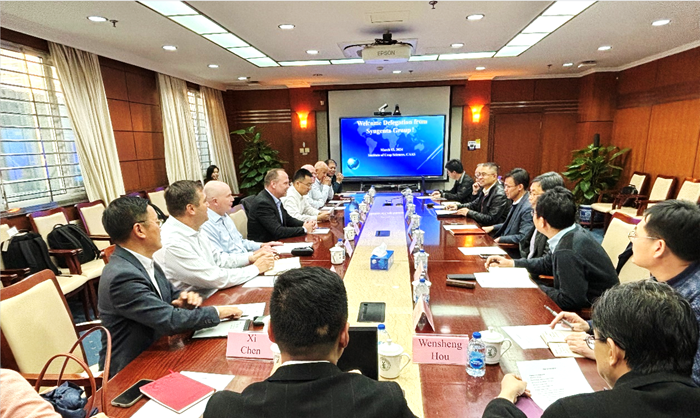 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
