A New Mechanism for MiRNA to Improve Salt Tolerance in Maize
Recently, Wang Lei and his colleagues from Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (BRI, CAAS) have discovered a new mechanism of miR169-mediated salt response. The results were published in Plant Physiology.
Salt stress is one of the factors that reduces the productivity of crop plants including maize. At present, the total area of saline-alkali land in China reaches 100 million hectares, accounting for 10.3% of the land area. Maize is the largest planted crop in China. Mining and identifying genes with salt tolerant in corn and clarifying its regulation network is of great significance to provide gene sources for the molecular design breeding in maize.
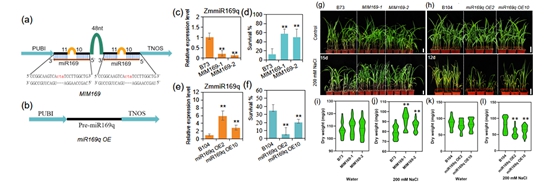
MiRNAs are major regulators of plant growth and stress responses, but few studies have examined the potential impacts of miRNAs on salt stress responses in maize. Researchers found that ZmmiR169q was responsive to stress-induced ROS signals. Salt stress and exogenous H2O2 treatment reduced the accumulation of ZmmiR169q, stress assays with transgenic materials showed that depleting ZmmiR169q increased seedling salt tolerance whereas overexpressing ZmmiR169q decreased salt tolerance. They found that ZmmiR169q repressed the transcript abundance of its target ZmNF-YA8, and overexpression ZmNF-YA8 in maize improved salt tolerance, specifically by transcriptionally activating the expression of PEROXIDASE1. This study reveals a direct functional link between salt stress and a miR169q-NF-YA8 regulatory module that plants use to manage ROS stress and strongly suggests that ZmNF-YA8 can be harnessed as a resource for developing salt-tolerant crop varieties.
Xing Lijuan and Zhu Ming contributed equally to the article, and Wang Lei and Xu Miaoyun from BRI were the co-corresponding authors.
This work was supported by National Key Research and development Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
By Wang Lei (wanglei@caas.cn)
-
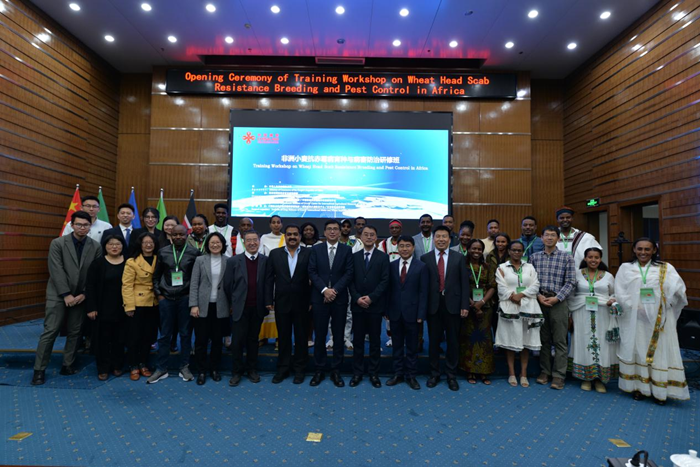 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
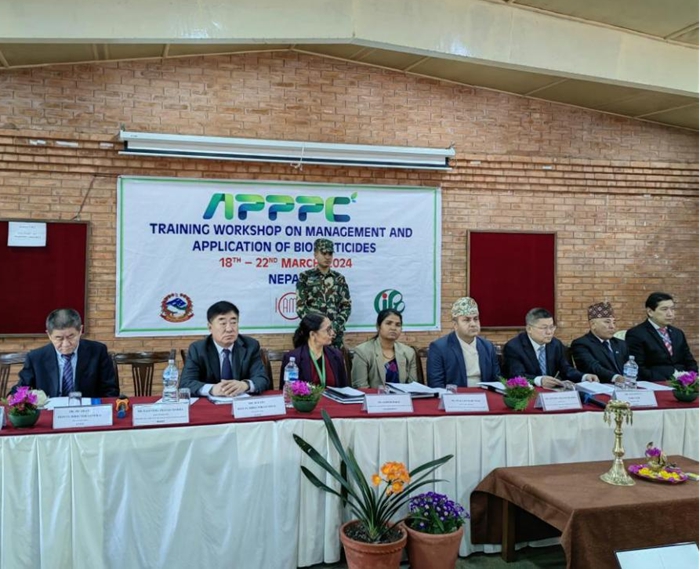 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
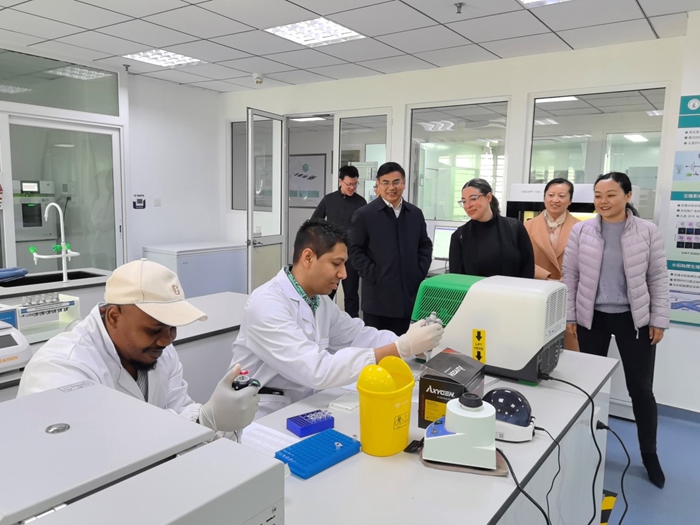 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
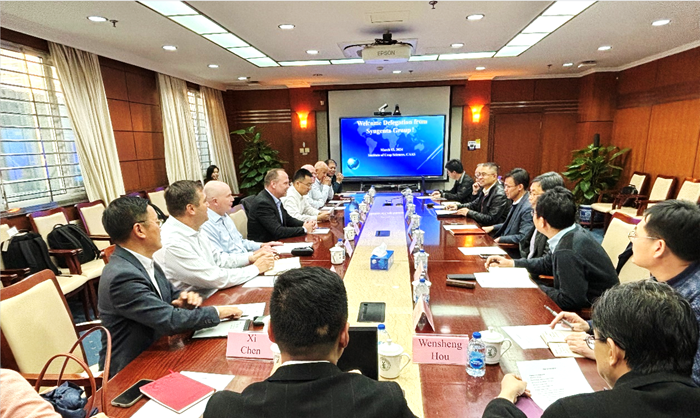 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
