The new progress of gene identifying associated with fruit domestication traits in peach through comparative population genomics study
Crop evolution is a long-term process involving selection by natural evolutionary forces and anthropogenic influences; however, the genetic mechanisms underlying the domestication and improvement of fruit crops have not been well studied to date. An important research progress which described selection sweeps and candidate genes associated with fruit domestication traits in peach through comparative population genomics study was achieved by the research team headed by Wang Lirong at the Zhengzhou Fruit Research Institute and published in Plant Biotechnology Journal on April 5, 2019.
In this study, by using multiple populations and tissues, the research team performed several RNA-seq analyses in peach and found that the up-regulation of selection genes during domestication occurred mostly in fruit and seeds. However, during the improvement stage, more up-regulated selection genes were identified in leaves and seeds than in the other organs (Figure 1).
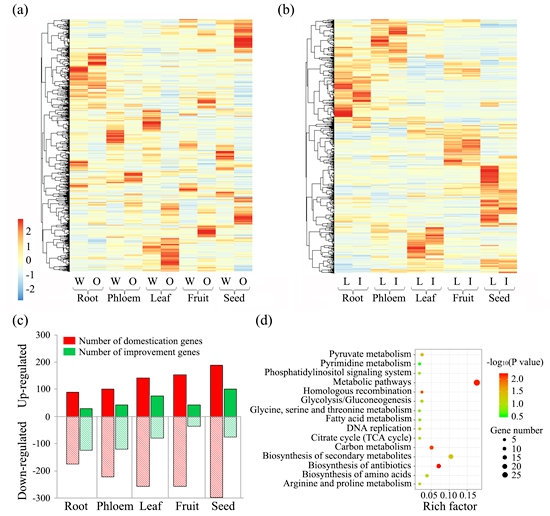
Figure 1. Tissue-specific expression of genes from four groups of peaches
Meanwhile, the researche team identified 9, 21, 11, 9, 23, 28, 22 and 48 association signals for the traits of fruit size,stone size, fruit/stone weight, flesh adhesion/texture, SSC/titratable acidity (TA), and acid, sugar and polyphenol contents, respectively, using a linear mixed model with 988 306 filtered SNPs with high-throughput efficiency. Among these loci, three candidate genes (Prupe.6G046800, Prupe.4G191900, and Prupe.2G087000) were highly associated with fruit weight and the sorbitol and catechin content in fruit after studying their expression and genotypes (Figure 2).
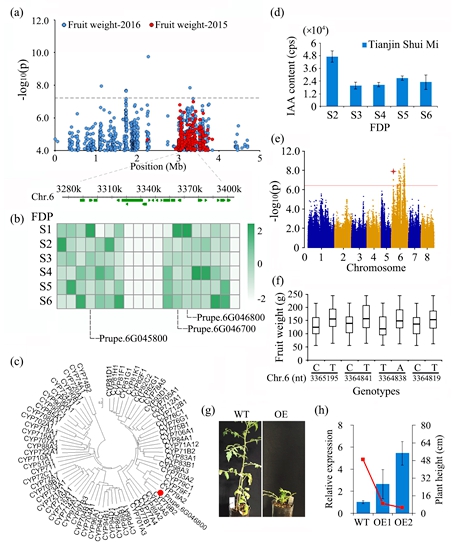
Figure 2. Association results for fruit weight and the expression profiles of candidate genes
Finally, analyzing the allele frequency of each associated SNP for each trait demonstrated that there is genetic potential for the breeding of more nutritious fruit with enhanced bioactive polyphenols without disturbing a harmonious sugar and acid balance by crossing with wild species.
The paper was a continuous study after they published the paper in Genome Biology in 2014 and 2019 and Nature Communications in 2016 under the project “1000 peach genomes”. This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD1000200) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2016-ZFRI-01).
The URL for this article should be:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pbi.13112
By Cao Ke (wyandck@126.com)
Edited by Yanjun Wang
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
