Study reveals that combined application of sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and pig manure simultaneously reduce cadmium and arsenic in rice and improves soil quality
Recently, the Remediation of Degraded and Contaminated Farmland Team from the Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, revealed that the combined application of sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI) and pig manure (PM) can effectively reduce cadmium and arsenic content in rice and improve soil quality at the same time. The related research findings have been published in the Environmental Technology & Innovation.
The safe utilization of rice fields contaminated by cadmium and arsenic is a key focus in the management of agricultural soil heavy metal pollution. Research indicates that iron-based materials can be used for effective in-situ remediation of rice fields contaminated by cadmium and arsenic. However, the impact of these materials on soil quality while achieving cadmium and arsenic fixation remains unclear.
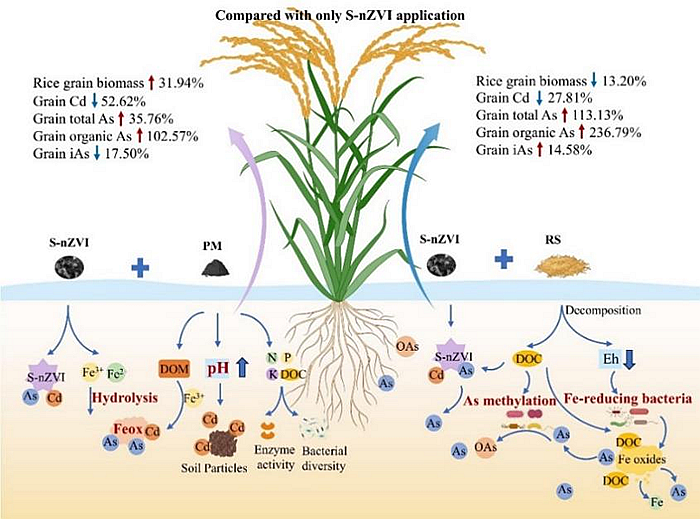
This study investigated the effects of combined application of S-nZVI and different organic amendments on Cd and As content in various rice tissues and soil quality. The results demonstrated that the combined application of S-nZVI and PM significantly reduced Cd (78.95%) and As (68.69%) content in rice grains, bringing both below the Chinese food safety standard (0.2 mg·kg⁻¹). The application of S-nZVIcan increase soil pH and effectively immobilize arsenic and cadmium in the soil byincreasing the content of amorphous iron oxide and providing arsenic-cadmium complexation sites. Furthermore, the combined application of S-nZVI and PM can significantly enhance functional enzyme activity, increase bacterial community diversity, and promote rice yield. However, the combined application of S-nZVI and rice straw (RS) can lead to arsenic methylation in the rice field soil, increasing the total arsenic and organic arsenic content in the rice. Therefore, caution is advised when applying S-nZVI+RS in As-contaminated rice fields. This study provides theoretical support for the safe utilization of Cd- and As-co-contaminated rice fields, contributing to ensuring the quality and safety of agricultural products and improving the health of cultivated soil.
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Jiangxi Provincial Key Research and Development Program and the Science Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science.
Linkage:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2024.103942
-
 Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation
Jan 21, 2025IAED-CAAS Delegation Visits Thailand for Scientific Cooperation -
 Dec 12, 2024Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) is launching the NARS Capacity Building through China-Africa Research Partnership Program
Dec 12, 2024Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) is launching the NARS Capacity Building through China-Africa Research Partnership Program -
 Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland
Dec 05, 2024China-CABI Project Development Workshop Held in Delémont, Switzerland -
 Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS
Dec 05, 2024Ministerial Workshop on Digital Agriculture and Rural Revitalization for BRI Partner Countries Held at CAAS -
 Dec 05, 2024CIAR and FGV Deepen Cooperation to Promote the Development of China-Brazil Green Agricultural Products Value Chain
Dec 05, 2024CIAR and FGV Deepen Cooperation to Promote the Development of China-Brazil Green Agricultural Products Value Chain
