Study reveals mechanism of melatonin enhancing wheat drought and salt resistance
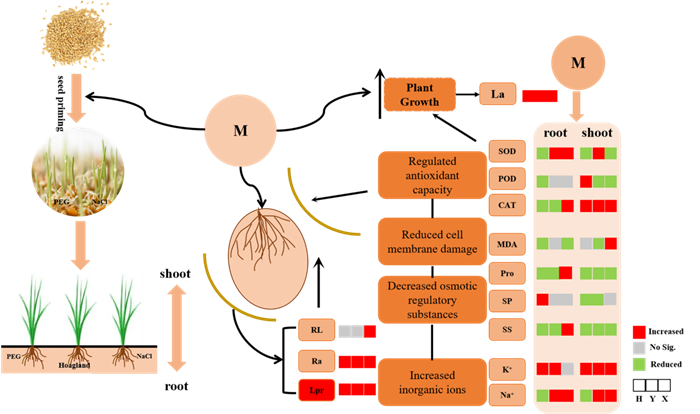
Recently, the Principles and Technologies for Deficit Irrigation Team from the Institute of Farmland Irrigation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences made new progress in the study of mechanism of melatonin enhancing wheat drought and salt resistance. The study reveals that melatonin improves the root hydraulic conductivity of wheat under drought, salt, and drought-salt stresses by modulating translation levels of aquaporin genes and contributed root elongation and seedlings growth. The related research findings have been published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
The root hydraulic conductivity of three wheat varieties from no-priming was significantly reduced under PEG, NaCl, and PEG + NaCl stresses. The present study suggested that melatonin priming was a strategy as regards the enhancement of root hydraulic conductivity under PEG, NaCl, and PEG + NaCl stresses, which efficiently enhanced wheat resistant to drought-salinity stress.
Proposed mechanism of action underlying the enhancement of seedling growth by melatonin priming under PEG + NaCl stress
This study was supported by the Major Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, the National Key Research and Development Project, the China Agriculture Research System of MOA and MARA, the Key Scientific and Technological Projects of Henan Province, and the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund.
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/9/5055
By: Li Penghui (lipenghui@caas.cn)
-
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Deputy Director General of IAEA
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Deputy Director General of IAEA -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Chairman of the Understanding China Forum
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Chairman of the Understanding China Forum -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Greek Minister
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Greek Minister -
 May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Iranian First Deputy Minister of Agriculture
May 29, 2024CAAS President Meets Iranian First Deputy Minister of Agriculture -
 May 28, 2024The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection was further strengthened
May 28, 2024The Lao PDR-China Joint Laboratory for Plant Protection was further strengthened
