New progress in the discovery of endophytic microbial resources of specialty cash crops
Recently, the Green Low-Carbon Production Technology Innovation Team from the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IBFC, CAAS) isolated a broad-spectrum and highly effective endophytic Bacillus velezensis SEC-024A from the leaf tissue of industrial hemp. Through series of experiments, the study analyzed the mechanism of inhibition and screened the active substances.
Hemp ( Cannabis sativa L.) is globally cultivated for agricultural and industrial purposes. It is widely used to produce pharmaceuticals, textiles, biofuels, building materials, paper products, insulation materials, etc. The increase in production of C. sativa has been associated with rising frequency and severity of fungal diseases, including the emergence of new diseases, i.e., root, crown and bud rot induced by Fusarium , Botrytis and Sclerotinia in hemp. Biological control has emerged as an efficient and sustainable method that uses beneficial microorganisms or microbial metabolites to control this disease.
An endophytic bacterium SEC-024A was isolated from the leaf tissue of industrial hemp. SEC-024A exhibited a significant antagonistic effect on A. rolfsii , with a plate inhibition rate of 80.5% and a pot control effect of 74.1%, and effectively suppressed the growth of various phytopathogens, including Magnaporthe oryzae , Thanatephorus cucumeris , and Ralstonia solanacarum , etc, representing a promising candidate from which to develop a control agent against this disease. Genome-wide analysis revealed that SEC-024A has abundant secondary metabolite synthesis-related gene clusters, the effective inhibitory component test further revealed that the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by SEC-024A strain play a key role in the inhibitory antagonistic process. Four compounds were founded exhibiting efficient inhibitory effects on pathogens from the VOCs of SEC-024A-isobutyric acid, tiglic acid, trans-2-octenal, and 2-decanone, whose EC50 values against A. rolfsii , were respectively 0.012, 0.038, 0.009 and 0.046 μL/mL, respectively. Trans-2-octenal was verified to show broad-spectrum inhibitory activity against soilborne disease pathogens of various cash crops. B. velezensis SEC-024A holds promise as a novel microbial agent for controlling diseases.
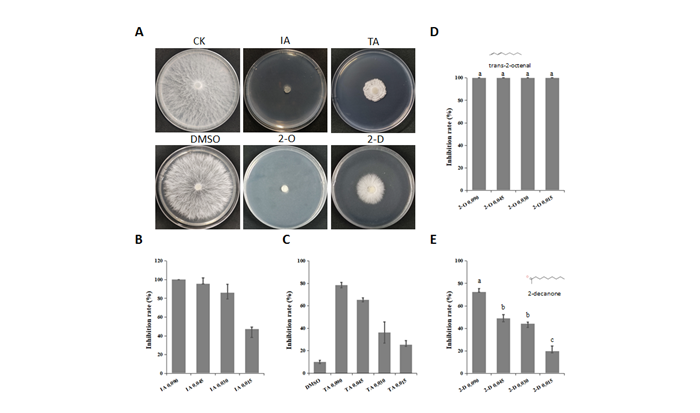
Fig. Negative impacts of VOCs generated by SEC-024A on A. rolfsii .
This research was funded by the Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) and the Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Agricultural Biogenomics of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
The study titled “ Biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis SEC-024A against southern blight of industrial hemp ” has been published online in “Industrial Crops & Products” and can be accessed through the link : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926669024017448
-
 Nov 06, 2024Experts from ICS Participated in the 3rd IWC
Nov 06, 2024Experts from ICS Participated in the 3rd IWC -
 Oct 24, 2024Prof. Luxiang Liu Renewed His Term as the Chairman of the Mutation Breeding Network (MBN)
Oct 24, 2024Prof. Luxiang Liu Renewed His Term as the Chairman of the Mutation Breeding Network (MBN) -
 Oct 23, 2024IPPCAAS Wins the 2024 FAO Achievement Award
Oct 23, 2024IPPCAAS Wins the 2024 FAO Achievement Award -
 Oct 23, 2024ICS Hosted the Symposium of China-European Union Nature-based Solutions for Nutrient Management International Cooperation Program
Oct 23, 2024ICS Hosted the Symposium of China-European Union Nature-based Solutions for Nutrient Management International Cooperation Program -
 Sep 30, 2024China-Laos Training Workshop on Integrated Management of Major Crop Pests and Diseases Concludes Successfully in Laos
Sep 30, 2024China-Laos Training Workshop on Integrated Management of Major Crop Pests and Diseases Concludes Successfully in Laos
