Development of nutritious rice with high zinc/selenium and low cadmium in grains through QTL pyramiding
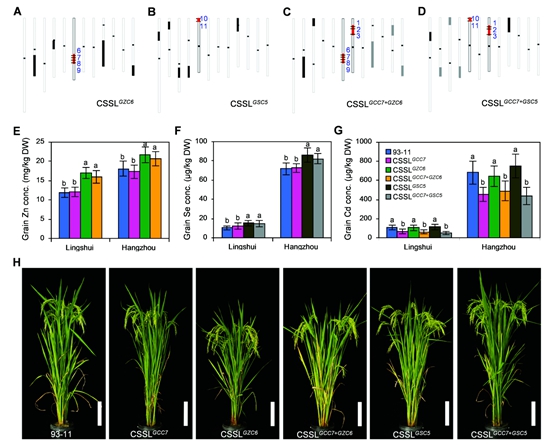
Enriching zinc (Zn) and selenium (Se) levels, while reducing cadmium (Cd) contcentration in rice grains is of great benefit for human diets and health. The large natural variations in grain Zn, Se and Cd concentrations in different rice accessions enable Zn/Se biofortification and Cd minimization through molecular breeding. Recently, in a paper entitled “Development of nutritious rice with high zinc/selenium and low cadmium in grains through QTL pyramiding” published in Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, the germplasm innovation research team from China National Rice Research Institute (CNRRI) reported that the development of new elite varieties by pyramiding major QTLs significantly contributed to high Zn/Se and low Cd accumulation in grains.
CSSLGCC7, a chromosome segment substitution line with the PA64s-derived GCC7 allele in the 93-11 background, exhibited steadily higher Mn and lower Cd concentrations in grains than those of 93-11. This elite CSSL was used as the core breeding material to cross with CSSLs harboring other major QTLs for essential mineral elements, especially CSSLGZC6 for grain Zn concentration and CSSLGSC5 for grain Se concentration. The CSSLGCC7+GZC6 and CSSLGCC7+GSC5 exhibited lower Cd concentration with higher Zn and Se concentrations in grains, respectively. The study thus provides elite materials for rice breeding targeting high Zn/Se and low Cd concentrations in grains.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91735304 and 31671761) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0100902-07). Click on the link below for more details:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jipb.12909
By Shen Huizhi(shenhuizhi@caas.cn)/Liu Chaolei(liuchaolei@caas.cn)
-
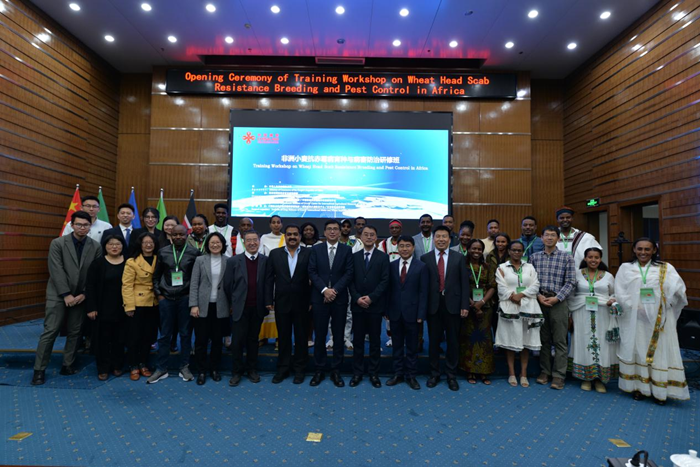 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
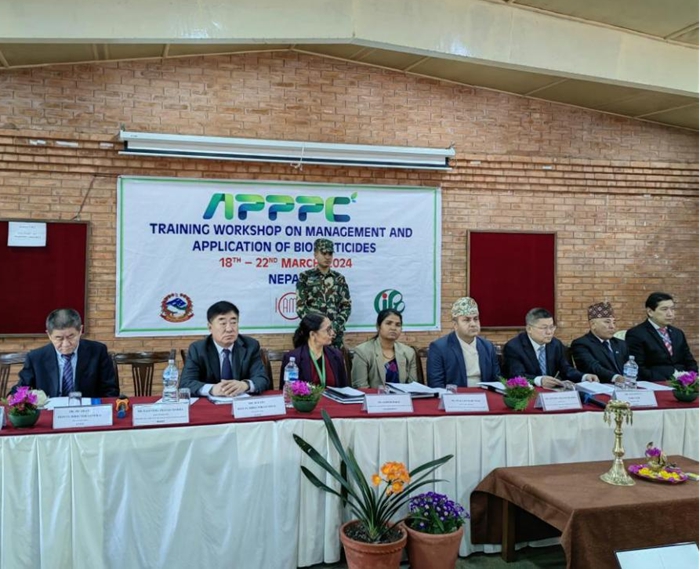 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
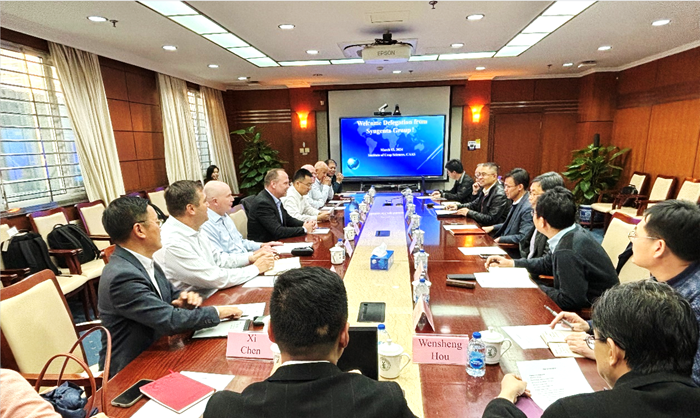 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
