Structural Conversion of Pectin Fractions During Heat Processing in Relation to the Ability of Inhibiting Lipid Digestion:
Recently, the innovation team for fruit and vegetable processing and quality control of the Institute of Food Science and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (IFST, CAAS), has used the hawthorn as an object for investigating the relation of structural conversion of pectin fractions during heat processing to the ability of inhibiting lipid digestion. The relevant research results were published in Food Hydrocolloids with the title “Structural conversion of pectin fractions during heat processing in relation to the ability of inhibiting lipid digestion: A case study of hawthorn pectin”.
In this study, pectin fractions including water-soluble pectin (WSP), chelator-soluble pectin (CSP), and Na2CO3-soluble pectin (NSP) were isolated from hawthorn tissue after heat processing for different duration, as well as the dissolved pectin (DSP) in the heating aqueous phase. The structural features of pectin fractions were characterized by degree of methoxylation, neutral sugar composition, and molecular weight (MW) distribution. After 30-min heat processing, the amount of WSP increased from 78 to 111 mg/g dry basis, while those of CSP and NSP decreased, meanwhile certain amount of DSP (68 mg/g dry basis) was generated. During heat processing, a dynamic alteration of pectin fractions involving solubilization and depolymerization occurred. The solubilization mainly occurred in CSP and NSP, inducing a shift from water-insoluble pectin to WSP. The depolymerization occurred in homogalacturonan region of WSP, resulting in a formation of DSP. With the increasing heat duration, a more pronounced depolymerization appeared in DSP, which resulted in forming a large amount of pectic polysaccharide fragments with small MW. The WSP showed a good rheological behavior and an ability to inhibit lipid digestion, which was higher than those of DSP. The inhibition rate of WSP (0.1% (w/w)) on lipid digestion decreased from 48.5 % to 11.2 % after 30-min heat processing. The results can provide novel knowledge to better understand the relation between structure and function of pectin in heat processing.
Assistant researcher Zhou Mo is the first author. Professor Bi Jinfeng and Professor Aurore Richel from University of Liège are co-corresponding authors. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2020-IFST-04) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (S2020JBKY-17).
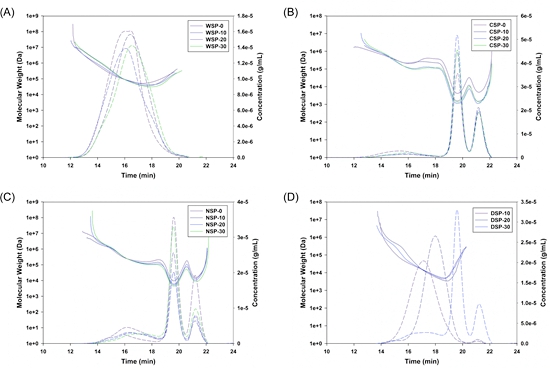
Fig. 1. Molar mass distribution (solid line) and concentration (dash line) of water-soluble pectin (A), chelator-soluble pectin (B), Na2CO3-soluble pectin (C), and the dissolved pectin fraction (D) in aqueous phase) during heat processing at 100 °C.
Link to the paper:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106721
By Jin Xin (jinxin@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
