Biodegradable poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) microcapsules for controlled release of trifluralin with improved photostability and herbicidal activity
Weeds are quite common in agricultural plantations, which have an adverse effect on quality and yield of agricultural product. Herbicide application is the most widely used method to cope with the adaptive advantages of weeds and improve the priority growth of desired crops. However, due to the application method and environmental conditions, most of the used herbicides fail to reach the target site or run off into the environment. Trifluralin, commonly used as a selective pre-emergence herbicide, is subject to loss by volatilization and decomposition when applied to the surface of soils. which raise production cost and lead to negative effects on the natural ecosystem. Microencapsulation of pesticide is a promising technology to reduce the negative environmental impact and benefit the sustainable development.
Recently, a research group at the Key Laboratory of Integrated Pest Management in Crops, IPP-CAAS published a research paper on Materials Science & Engineering C, reporting the preparation of trifluralin microcapsules by a convenient solvent evaporation method using biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) polymers as carriers. When performed under the optimized conditions, the corresponding loading content and encapsulation efficiency of trifluralin were 16.50% and 90.65%, respectively. The release of trifluralin from PHB microcapsules showed slow and sustained patterns, which could be easily achieved by modifying the preparation parameters including shearing speed and concentration of emulsifier. Compared to conventional trifluralin formulation of emulsifiable concentrate, trifluralin microcapsules exhibited significantly improved photostability and herbicidal activity against target weed barnyardgrass. These results demonstrated that microencapsulation with PHB could dramaticlly improve the effective utilization rate and decrease the dosage of such agricultural chemicals.
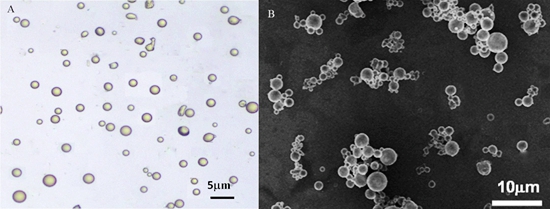
Optical microscope (A) and SEM (B) images of PHB trifluralin microcapsules

Bioactivity for target barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) (A) treatment with trifluralin microcapsules, (B) treatment with trifluralin EC, and (C) control without herbicide.
More details are available on the links below:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493118324676
by Cao Lidong(caolidong@caas.cn)
-
 Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS
Apr 18, 2024Opening Ceremony of the Training Workshop on Wheat Head Scab Resistance Breeding and Pest Control in Africa Held in CAAS -
 Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal
Apr 03, 2024IPPCAAS Co-organized the Training Workshop on Management and Application of Biopesticides in Nepal -
 Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS
Mar 28, 2024Delegation from the School of Agriculture and Food Science of University College Dublin, Ireland Visit to IAS, CAAS -
 Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS
Mar 25, 2024Director of World Food Prize Foundation visited GSCAAS -
 Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
Mar 20, 2024Institute of Crop Sciences (ICS) and Syngenta Group Global Seeds Advance Collaborative Research in the Seed Industry
